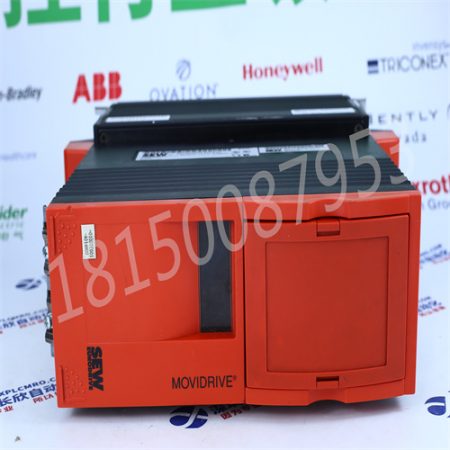
SEW 31C005-503-4-00
The SEW 31C005-503-4-00 is a product with the following information content and parameters:
- Information Content: This refers to the amount and type of information that can be stored and transmitted by the product.
- Parameters: Parameters are specific characteristics or features of the product that can be adjusted or set according to the requirements or specifications. The parameters of the SEW 31C005-503-4-00 may include:
- Voltage Range: The allowable range of input voltage for the product.
- Power Consumption: The amount of power the product consumes during operation.
- Operating Temperature Range: The range of temperature within which the product can function properly.
- Dimensions: The physical size and measurements of the product.
- Weight: The weight of the product.
- Input/Output Interfaces: The types of interfaces available for connecting the product to other devices or systems.
- Frequency Response: The range of frequencies over which the product can operate effectively.
- Output Power: The maximum power output of the product.
- Control Options: The different ways in which the product can be controlled or operated.
- Safety Features: Any built-in safety features or protections provided by the product.
These parameters may vary depending on the specific model and version of the SEW 31C005-503-4-00 product. It is always recommended to refer to the product documentation or contact the manufacturer for detailed and up-to-date information about the specific product.

ABB MOTOR STARTER RELAY 7.5 AMP 120 V MODEL B16-30-10
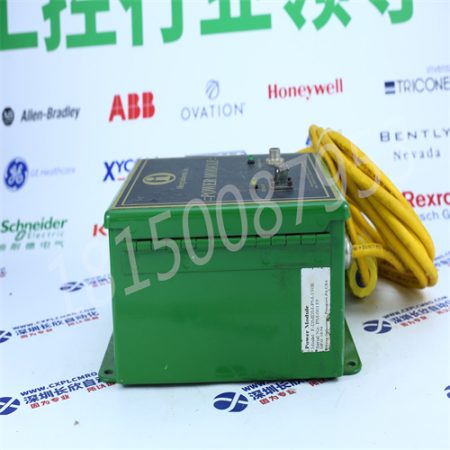
ASEA ABB FLEX MODULE POWER AMPLIFIER YL261001-LL 2668
ABB GE TAYLOR FANUC GENIUS 6228BZ10000D
ABB Circuit Breaker S3H 3P 600VAC/DC 15A
ABB Asea Brown Boveri BC9/CA7-22E Contactor
ABB CIRCUIT BREAKER RT-926,MF719626
ABB K4PF Plug In Kit

Basic structure of single-phase asynchronous motors
A single-phase asynchronous motor is a motor that only requires single-phase AC power supply [2]. A single-phase asynchronous motor is composed of a stator, rotor, bearing, casing, end cover, etc. The stator is composed of a base and an iron core with windings. The iron core is formed by punching and laminating silicon steel sheets, and two sets of main windings (also known as operating windings) and auxiliary windings (also known as starting windings to form auxiliary windings) are embedded in the slots at a 90 ° electrical angle. The main winding is connected to an AC power source, and the auxiliary winding is connected in series with a centrifugal switch S or starting capacitor, operating capacitor, etc. before being connected to the power source. The rotor is a cage type cast aluminum rotor, which is made by laminating the iron core and casting aluminum into the groove of the iron core, and casting the end ring together to short-circuit the rotor guide bar into a squirrel cage type.
Single-phase asynchronous motors are also divided into single-phase resistance starting asynchronous motors, single-phase capacitor starting asynchronous motors, single-phase capacitor running asynchronous motors, and single-phase dual value capacitor asynchronous motors.
Basic structure of three-phase asynchronous motors
Three phase asynchronous motors mainly consist of stator, rotor, and bearings [3]. The stator mainly consists of an iron core, three-phase winding, frame, and end cover. The stator core is generally made of 0.35-0.5mm thick silicon steel sheets with an insulation layer on the surface, which are punched and laminated. There are evenly distributed grooves in the inner circle of the core for embedding the stator winding. The three-phase winding is composed of three identical windings arranged at an electrical angle of 120 ° apart in space, with each coil embedded in each slot of the stator according to a certain pattern. Its function is to apply three-phase alternating current, generating a rotating magnetic field. The frame is usually made of cast iron, while the frame of large asynchronous motors is usually welded with steel plates. The frame of micro motors is made of cast aluminum, which is used to fix the stator core and front and rear end covers to support the rotor, and to provide protection, heat dissipation, and other functions. There are heat dissipation ribs on the outside of the enclosed motor base to increase the heat dissipation area, and ventilation holes are opened on the end covers of the protective motor base at both ends, allowing direct convection of air inside and outside the motor to facilitate heat dissipation. The end cover mainly serves to fix the rotor, support and protect it. The rotor mainly consists of an iron core and a winding. The material used for the rotor core is the same as the stator, which is made of 0.5mm thick silicon steel sheets punched and laminated. The outer circle of the silicon steel sheets is punched with evenly distributed holes to accommodate the rotor winding. Usually, the stator core is used to punch the inner circle of the lagging silicon steel sheet to make the rotor core. Generally, the rotor core of small asynchronous motors is directly pressed onto the shaft, while the rotor core of large and medium-sized asynchronous motors (with a rotor diameter of over 300-400 millimeters) is pressed onto the shaft with the help of a rotor bracket. The rotor winding is divided into squirrel cage rotor and wound rotor. (1) Squirrel cage rotor: The rotor winding is composed of multiple guide bars inserted into the rotor slot and two circular end rings. If the rotor core is removed, the entire winding will look like a squirrel cage, hence it is called a cage winding. Small cage motors use cast aluminum rotor windings, and for motors above 100KW, they are welded with copper bars and copper end rings. The squirrel cage rotor is divided into several types: impedance rotor, single squirrel cage rotor, double squirrel cage rotor, and deep groove rotor, with different starting torque and other characteristics. (2) Wound rotor: The wound rotor winding is similar to the stator winding and is also a symmetrical three-phase winding. It is generally connected in a star shape, and the three outlet heads are connected to the three collector rings of the shaft, and then connected to the external circuit through an electric brush.
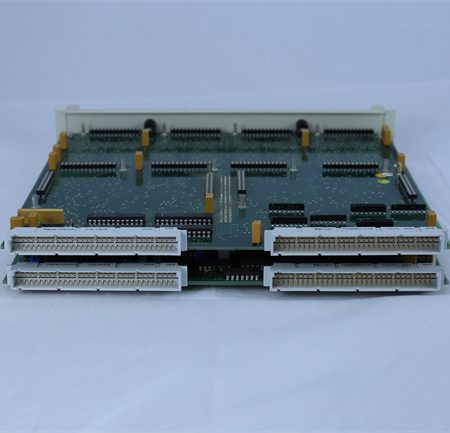
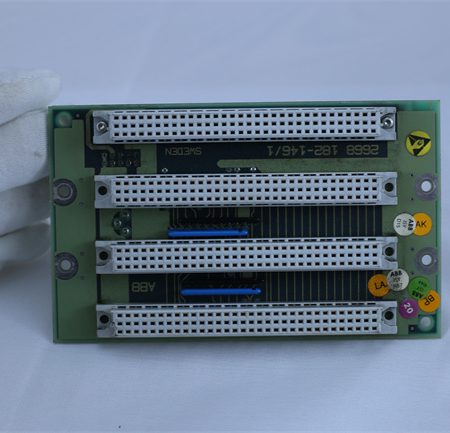














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.